26.11.2013, 14:36
(
Последний раз редактировалось BigETI; 01.12.2013 в 22:34.
)
Intro
As I've released an include called "Linked lists in PAWN", also an plugin called "Memory access plugin", which is required for the "Linked lists in PAWN" include, and obviously the majority of this community don't know the use and benefits of those releases, so I've decided to write this tutorial.Index
Quote:
|
Definition of a linked list
A linked list is basicly something, which can store nodes aka "blocks of memory" inside a list. Each node has links aka "pointers" to its next and previous nodes.By default nodes inside linked lists do not have IDs!
Abstract image of a linked list:
Quote:
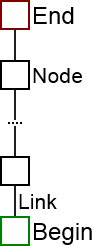 |
More about the "Linked lists in PAWN" include
This include allows you to store almost infinite (of course depends on your server's memory) amount of nodes inside linked lists.Also it comes with various functions to manipulate your lists, or store them each as a file. Those files are not meant to be human readable, hence should only be modified, if you know what you are actually doing!
This include relies on the "Memory access" plugin, to handle dynamic memory.
What is "dynamic memory"?
Actually "dynamic memory" is memory you can allocate and free in runtime.It's highly recommended, if the size of requested blocks of memory becomes unpredictable.
More about the "Memory access" plugin
There will be a proper tutorial about the "Memory access" plugin in the future.Meanwhile you can check this thread: https://sampforum.blast.hk/showthread.php?tid=451381
"Pro"s and "Con"s of the "Linked lists in PAWN" include
Pro:Quote:
|
Quote:
|
What can I do for my server by using linked lists?
Some examples:Quote:
|
How to use the "Linked lists in PAWN" include
You've probably asked yourself, how to use this include and what functions does it give us.I've already spend a lot of time to create a proper documentation at the "Linked lists in PAWN" release thread. You should take a bite from it. https://sampforum.blast.hk/showthread.php?tid=451962
Here I'll explain you some basics this include gives us:
Creating a valid linked list
pawn Код:
new List::init<my_list>; // Declares an empty linked list
Creating nodes inside a linked list (simple)
pawn Код:
// Declares an empty linked list
new LIST::init<my_list>;
// Creates a node and adds the number 5 in it
LIST::push_back(my_list, 5);
// Creates a node and adds the number 7 in it
LIST::push_back(my_list, 7);
Creating nodes inside a linked list (blocks of memory)
pawn Код:
// Example structure
MEM::struct example_struct
{
example_struct_data_1,
Float:example_struct_data_2,
example_struct_data_3[5],
Float:example_struct_data_3[200]
}
//...
// Declares an empty linked list
new LIST::init<my_list>,
// Declares an array
example_buffer[example_struct];
// Creates a node and adds an constant array
LIST::push_back_arr(my_list, {20, 5, 8, 100});
// Creates a node and adds a valid PAWN string
LIST::push_back_arr(my_list, "Hello world!");
// Set "example_buffer" with different values
// Creates a node and adds an array
LIST::push_back_arr(my_list, example_buffer);
Clear a linked list
pawn Код:
// Declares an empty linked list
new LIST::init<my_list>;
// Do some operations...
// Clears the whole list
LIST::clear(my_list);
Iterate through nodes inside a linked list, get and set data
pawn Код:
// Declares an empty linked list
new LIST::init<my_list>,
// Declares a pointer
Pointer:data_ptr;
// Do some operations...
// Iterates through the list
LIST::foreach<my_list_it>(my_list)
{
// Stores data pointer
data_ptr = LIST_IT::data_ptr(my_list_it);
// Increments value by 1
MEM::set_val(data_ptr, MEM::get_val(data_ptr)+1);
}
Iterate through nodes inside a linked list, get and set data (arrays)
pawn Код:
// Example structure
MEM::struct example_struct
{
example_struct_data_1,
Float:example_struct_data_2,
example_struct_data_3[5],
Float:example_struct_data_3[200]
}
// Declares an empty linked list
new LIST::init<my_list>,
// Declares a pointer
Pointer:data_ptr,
// Declares a variable to store the size of an array
data_size,
// Placeholder
data_buffer[example_struct];
// Do some operations...
// Iterates through the list
LIST::foreach<my_list_it>(my_list)
{
// Stores data pointer
data_ptr = LIST_IT::data_ptr(my_list_it);
// Stores the data size
if((data_size = LIST_IT::data_size(my_list_it)) != sizeof data_buffer)
{
print("The data is not %d units long. | Node: 0x%x | Data Pointer: 0x%x | Size: %d", sizeof data_buffer, _:my_list_it, _:data_ptr, data_size);
continue;
}
// Gets an array
MEM::get_arr(data_ptr, _, data_buffer);
// Do some operations...
// Zero sets memory (just an example)
MEM::zero(data_ptr, data_size);
}
Handle linked lists inside linked lists
pawn Код:
new LIST::init<my_list>, LIST::init<nested_list>;
// Push data
LIST::push_back(nested_list, 2);
LIST::push_back(nested_list, 4);
LIST::push_back(nested_list, 8);
LIST::push_back(nested_list, 10);
// Stores the linked list into a linked list
LIST::push_back_arr(my_list, _:nested_list);
// Zero set pointers, makes now "nested_list" handle as a different list.
MEM::zero(MEM::get_addr(_:nested_list[0]), sizeof nested_list);
// Push data
LIST::push_back(nested_list, 200);
LIST::push_back(nested_list, 400);
LIST::push_back(nested_list, 800);
LIST::push_back(nested_list, 1000);
LIST::push_back_arr(my_list, _:nested_list);
// Zero set pointers, makes now "nested_list" handle as a different list.
MEM::zero(MEM::get_addr(_:nested_list[0]), sizeof nested_list);
// Push data
LIST::push_back(nested_list, 2000);
LIST::push_back(nested_list, 4000);
LIST::push_back(nested_list, 8000);
LIST::push_back(nested_list, 10000);
LIST::push_back_arr(my_list, _:nested_list);
//...
new LIST::init<buffer>, count;
// Iterate through "my_list"
LIST::foreach<my_list_it>(my_list)
{
// Get array from a node
MEM::get_arr(LIST_IT::data_ptr(my_list_it), _, _:buffer);
// Print node count
printf("%d. List:", ++count);
// Iterate through a nested linked list, and print its values
LIST::foreach<buffer_it>(buffer) printf(" Value: %d", LIST_IT::data_val(buffer_it, 0));
}
Handle mixed data (with nested linked lists)
pawn Код:
MEM::struct my_data_struct
{
my_data_1,
Float:my_data_2,
my_data_3[10],
LIST::init<my_data_4>
}
//...
// Declares a buffer
new LIST::init<my_list>, my_data[my_data_struct];
my_data[my_data_1] = 10;
my_data[my_data_2] = 10.0;
format(my_data[my_data_3], 10, "Something");
// Push data
LIST::push_back(my_data[my_data_4], 10);
LIST::push_back(my_data[my_data_4], 20);
LIST::push_back(my_data[my_data_4], 30);
LIST::push_back(my_data[my_data_4], 40);
LIST::push_back(my_data[my_data_4], 50);
// Push mixed data into "my_list"
LIST::push_back_arr(my_list, my_data);
// Zero sets buffer
MEM::zero(MEM::get_addr(my_data[0]), sizeof my_data);
my_data[my_data_1] = 1;
my_data[my_data_2] = 1.0;
format(my_data[my_data_3], 10, "Hello");
// Push data
LIST::push_back(my_data[my_data_4], 1);
LIST::push_back(my_data[my_data_4], 2);
LIST::push_back(my_data[my_data_4], 3);
LIST::push_back(my_data[my_data_4], 4);
LIST::push_back(my_data[my_data_4], 5);
// Push mixed data into "my_list"
LIST::push_back_arr(my_list, my_data);
//...
new buffer[my_data_struct];
// Iterate through "my_list"
LIST::foreach<my_list_it>(my_list)
{
// Get array from node
MEM::get_arr(LIST_IT::data_ptr(my_list_it), _, buffer);
// Print data
printf("my_data_1 = %d | my_data_2 = %.1f | my_data_3 = \"%s\"", buffer[my_data_1], buffer[my_data_2], buffer[my_data_3]);
// Iterate through a nested linked list, and print its values
LIST::foreach<inner_list_it>(buffer[my_data_4]) printf(" Value: %d", LIST_IT::data_val(inner_list_it, 0));
}
Script examples
Quote:
"Linked lists in PAWN" include - Trivia
Quote:
|
Best regards
~ BigETI



